Selection guide Aramid Honeycombs
|
Honeycomb type
|
Cell size
(mm)
|
Density
(kg/m³)
|
Dimensions
(mm)
|
Compressive strength
(MPa)
|
Shear strength
(MPa)
|
Shear modulus
(MPa)
|
Production tolerances
|
| bare |
stabilized |
Length |
Width |
Length |
Width |
Length
(mm)
|
Width
(mm)
|
Thickness
(mm)
|
Weight
(%)
|
Cell size
(%)
|
|
Aramid Honeycomb 40 kg/m³
AC-NH-3.2-40
|

|

|
3.2
|
40
|
1100 x 750
|
1.29
|
-
|
0.86
|
0.50
|
40.0
|
22.0
|
≥ 0
|
≥ - 5
|
± 0.2
|
± 10
|
± 5
|
|
Aramid Honeycomb 32 kg/m³
AC-NH-3.2-32
|

|

|
3.2
|
32
|
1300 x 2600
1300 x 650
|
0.64
|
-
|
0.68
|
0.41
|
36.0
|
20.0
|
≥ 0
|
≥ - 5
|
± 0.2
|
± 10
|
± 5
|
|
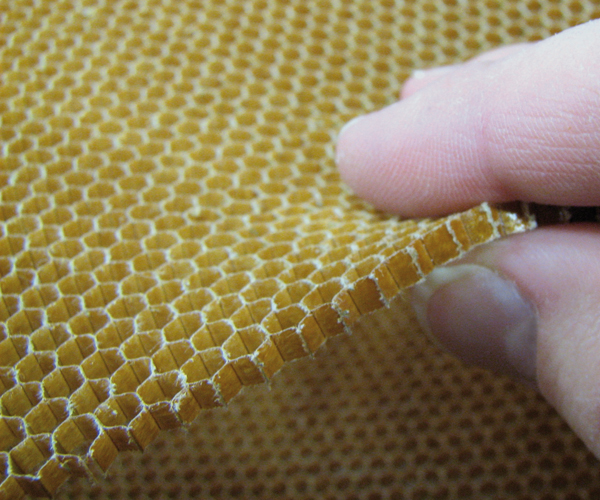
Aramid Honeycomb 29 kg/m³ (AERO)
C1 - 3.2 - 29
|
|

|
3.2
|
29
|
1120 x 2440
1120 x 1220
|
0.56
|
0.75
|
0.45
|
0.30
|
15.0
|
11.0
|
± 50
|
± 75
|
± 0.13
|
± 10
|
± 10
|
This is a dynamic table, by scrolling to the right all values become visible.
Aramid honeycombs
Aramid honeycombs are based on a bionic design.

Made of lightweight, phenolic resin-impregnated aramid paper, they have the highest compressive strength by weight of all support materials and very good chemical, impact, vibration, and fatigue resistance.
They are also very flexible and therefore suitable for components with spherical curves. Honeycombs are bonded under pressure, usually in a vacuum bag.
The honeycombs are used as core material between high-strength cover layers, which usually consist of glass or carbon laminates. This construction principle results in very stiff and lightweight components.
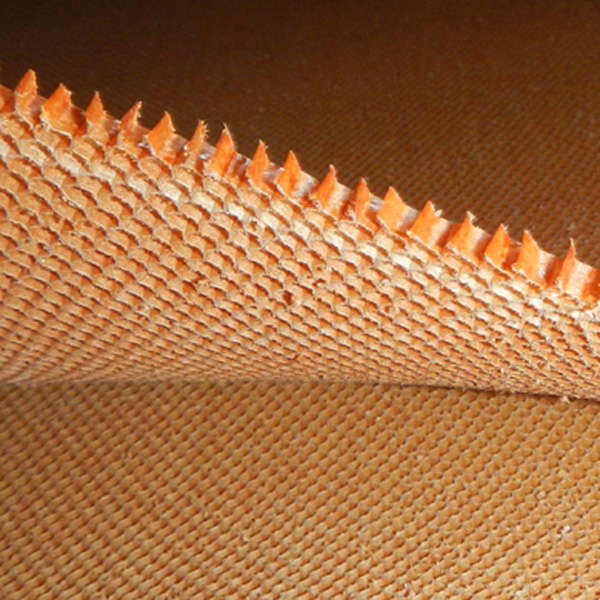
Hexagonal shape
The honeycombs usually have a hexagonal shape. The formability of thin sheets up to 3 mm is good but decreases with increasing thickness.
Industry-standard
Most honeycombs supplied by R&G meet the high industry standard. They are based on a Nomex® paper that is qualified for industrial use and is preferred for automotive, ship, and railroad construction and sports equipment.
Aero
There are also honeycombs with Aero approval, which have even tighter tolerances. They are based on Nomex® T 412 paper, which is qualified for aerospace applications.
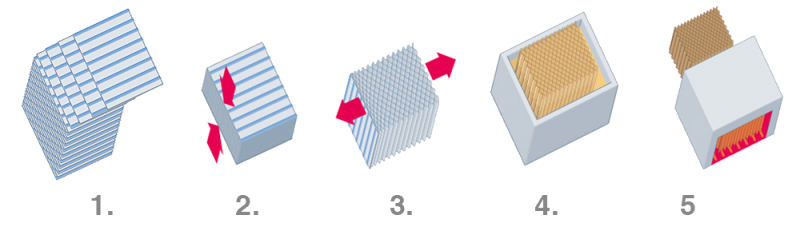
The production of honeycombs
1. Gluing
The aramid paper is printed with a special adhesive.
2. Pressing
The papers are placed on top of each other and pressed together. The applied adhesive causes the individual sides to bond together.
3. Expanding
The papers are pulled apart. The honeycomb block is formed.
4 + 5. Dipping and curing
The block is dipped in phenolic resin to give it its strength.
The block is cured in the oven.
This cycle is repeated until the desired density of the block is achieved. The higher the density, the higher the strength.
©Schütz